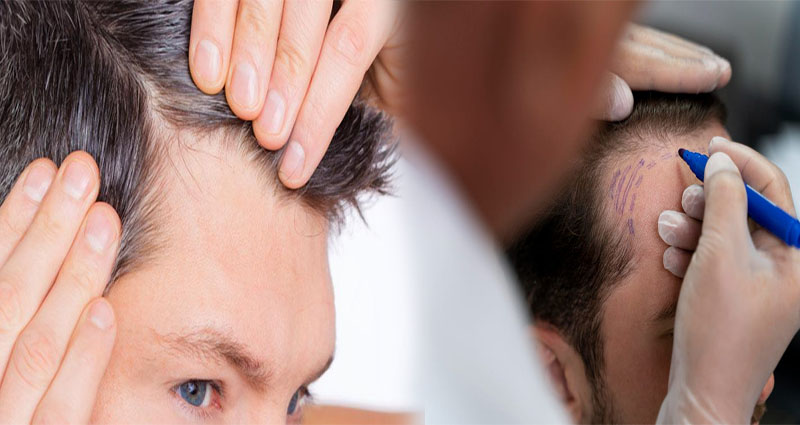
Hair transplant procedures have revolutionized the field of hair restoration, offering effective solutions for individuals experiencing hair loss or thinning. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) are two commonly performed hair transplant techniques, each with its own advantages and success rates. Understanding the differences between FUE and FUT can help individuals make informed decisions when considering a hair transplant procedure. Below is a comparison of the success rates of FUE and FUT techniques:
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Procedure: In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area using a specialized tool. These follicles are then transplanted to the recipient area where hair loss is present.
- Success Rate: FUE is known for its high success rate in hair transplantation. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure typically results in faster healing, minimal scarring, and a natural-looking hairline. The success rate of FUE largely depends on the surgeon’s skills and expertise in extracting and transplanting individual follicles.
- Recovery Time: Patients can expect a shorter recovery time with FUE compared to FUT. Most individuals can resume their regular activities within a few days to a week post-surgery.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- Procedure: FUT involves the removal of a strip of scalp tissue from the donor area, usually the back of the head. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation into the recipient area.
- Success Rate: FUT also boasts a high success rate in hair transplantation. The technique allows for the transplantation of a larger number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for individuals requiring extensive hair restoration.
- Scarring: One of the drawbacks of FUT is the linear scar that results from the extraction of the donor strip. While advancements in surgical techniques have minimized the appearance of scars, some individuals may still prefer the less visible scarring associated with FUE.
Key Differences:
- Scarring: FUE typically results in small, dot-like scars that are less noticeable, while FUT leaves a linear scar that may be visible in certain hairstyles.
- Number of Grafts: FUE is ideal for individuals requiring a smaller number of grafts, while FUT may be more suitable for extensive hair loss cases.
- Recovery Time: FUE generally offers a quicker recovery time compared to FUT, with minimal discomfort and downtime.
In conclusion, both FUE and FUT techniques have high success rates in hair transplantation, with each approach offering unique benefits. The choice between FUE and FUT ultimately depends on individual factors such as hair loss pattern, desired outcome, and personal preferences. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant surgeon is essential to determine the most suitable technique based on your specific needs and goals for achieving natural-looking and thicker hair.